Understanding gland valves and their applications is crucial for industries aiming for efficiency and safety in their operations. As noted by industry expert Dr. John Smith, a leading authority in fluid dynamics, "Gland valves play a pivotal role in controlling the flow and pressure within piping systems, making them indispensable in modern industrial processes." This statement emphasizes the importance of gland valves in maintaining operational integrity and reliability across various sectors, including oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, and water treatment.
Gland valves, designed to provide tight sealing while permitting movement within the system, are instrumental in managing the complexities associated with fluid conveyance. Their unique construction allows for effective handling of both high-pressure and aggressive media, ensuring that industries can operate smoothly while minimizing risks. By delving deeper into their functionality and applications, we can equip ourselves with the knowledge necessary to optimize valve selection and maintenance, ultimately enhancing operational performance.
In this guide, we will explore the various types of gland valves, their specific applications in different industrial contexts, and best practices for their maintenance. Understanding these elements is not only critical for engineers and decision-makers but also for anyone involved in the design and operation of fluid systems. As we journey through the intricacies of gland valves, we aim to demystify their role and highlight their significance in achieving industrial excellence.
Gland valves are integral components widely utilized in various industrial applications, primarily for controlling the flow of media. Defined as specialized valves that utilize a gland packing mechanism, their primary function is to prevent leaks and maintain pressure in systems. Unlike conventional valves, gland valves are designed to provide a robust sealing solution, making them ideal for environments where fluid containment is critical. The construction typically involves a movable stem and a packing material that compensates for wear over time, ensuring long-lasting performance.
The functionality of gland valves is particularly significant in industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, and water treatment. In these sectors, the ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures is essential. Additionally, gland valves can easily be adjusted to vary the degree of flow restriction, offering versatility in process control. Their design also facilitates ease of maintenance, allowing technicians to replace the packing material without having to remove the entire valve. This combination of durability, adaptability, and ease of service makes gland valves a preferred choice in applications where reliability and efficiency are paramount.
| Gland Valve Type | Definition | Functionality | Applications | Material Used | Pressure Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Valve | A valve that uses a spherical disc to control flow. | Provides on/off control with minimal resistance. | Oil and gas, water distribution, chemical processing. | Stainless steel, brass, plastic. | Up to 6000 psi. |
| Gate Valve | A valve that opens by lifting a barrier out of the path of fluid. | Allows for unobstructed flow when fully open. | Water supply, sewage treatment, oil pipelines. | Cast iron, carbon steel, stainless steel. | Up to 1500 psi. |
| Globe Valve | A valve with a globular body that regulates flow. | Offers good throttling capabilities. | Chemical plants, power generation, water systems. | Cast steel, stainless steel, bronze. | Up to 3000 psi. |
| Butterfly Valve | A valve that uses a rotating disc to regulate air or fluid flow. | Simple operation, quick opening and closing. | HVAC systems, water treatment, chemical services. | PVC, ductile iron, stainless steel. | Up to 250 psi. |
Gland valves play a crucial role in various industrial applications, particularly in controlling the flow of liquids and gases. There are several types of gland valves, each designed with unique features tailored to specific operational needs. The most common types include gate valves, globe valves, and butterfly valves. For instance, gate valves are particularly effective for on/off control, providing minimal pressure drop when fully open, making them ideal for high flow applications. According to a recent market analysis, the demand for gate valves in the oil and gas sector is projected to reach USD 8 billion by 2026, highlighting their essential role in energy transmission systems.
Globe valves, on the other hand, are known for their excellent throttling capabilities. They enable precise control of flow rate and are strategically utilized in steam systems and water treatment plants. Their design facilitates a higher pressure drop, but this can be an advantage in applications requiring stringent flow regulation. As per industry reports, the global globe valve market is expected to see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% over the next five years, reflecting an increasing trend towards efficient flow management in industrial processes.
Butterfly valves, with their quarter-turn mechanism, are favored for their lightweight and compact design. They are particularly effective in applications where space and weight are considerations, such as in HVAC systems and wastewater treatment facilities. The versatility of butterfly valves is underscored by a recent survey indicating an uptick in their adoption, especially in larger pipelines, driven by their ease of installation and maintenance. As industries continue to evolve, understanding the unique features of each valve type becomes essential for optimizing industrial processes and ensuring operational efficiency.
This bar chart illustrates the percentage of applications of different types of gland valves in various industrial sectors. Gate valves are the most commonly used, followed by ball valves and check valves. Each type has unique features suited for specific applications.
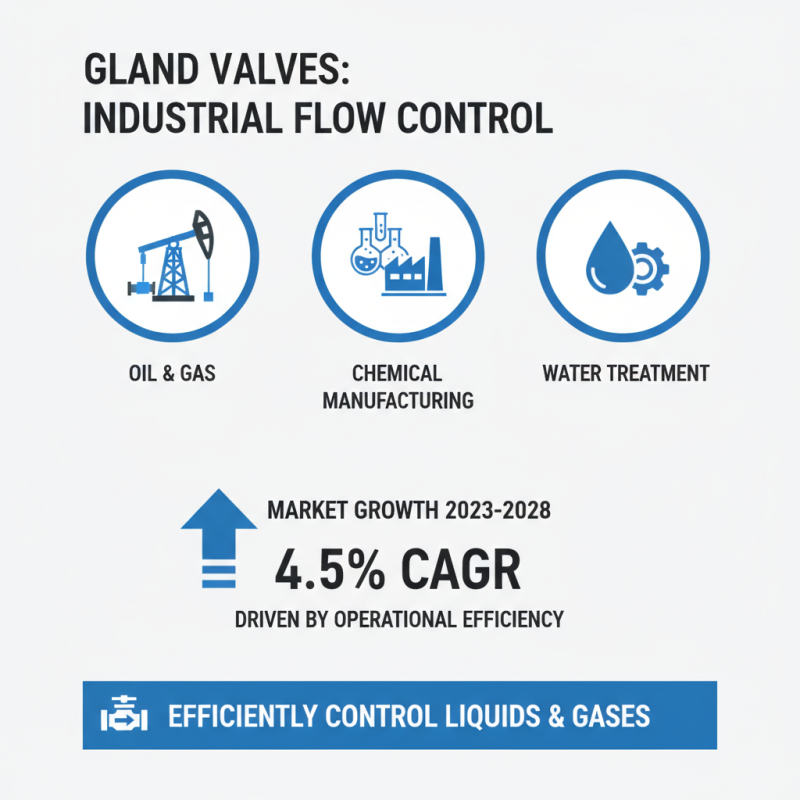
Gland valves play a crucial role in various industrial applications due to their ability to efficiently control the flow of liquids and gases in piping systems. These valves are commonly found in sectors such as oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, and water treatment. According to the latest industry analysis, the global market for gland valves is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2023 to 2028, driven by the increasing demand for effective flow control devices to enhance the operational efficiency of industrial processes.
In the oil and gas industry, gland valves are indispensable for managing high-pressure applications. They help maintain the integrity of the systems by providing reliable shut-off capabilities while preventing leaks. A report from the International Energy Agency highlights that stringent safety standards and regulations are propelling the need for advanced valve systems in oil and gas operations, with a forecasted increase in valve sales, significantly in harsh environments. Moreover, in the chemical manufacturing sector, gland valves are used for handling corrosive substances, where their robust design helps withstand extreme conditions, thus ensuring safe and uninterrupted operations. By facilitating precise flow regulation, these valves contribute heavily to optimized production processes across multiple industrial environments.

The installation and maintenance of gland valves are critical to ensuring their efficient operation in various industrial applications. Proper installation requires a comprehensive understanding of valve specifications and operating conditions. According to a report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), improper installation can lead to a significant increase in downtime and maintenance costs, with estimates suggesting that poor valve installation alone accounts for nearly 30% of overall maintenance expenditures in industrial settings.
Maintenance best practices for gland valves encompass regular inspections, leak tests, and timely replacements of worn components. The valve's packing material should be checked periodically, as it plays a crucial role in preventing leaks and ensuring safe operation. A study published by the Chemical Engineering Research Journal indicates that valves with well-maintained gland packing can extend their operational lifespan by up to 40%, reducing the frequency and cost of replacements. Furthermore, training personnel on the specific requirements for gland valve care can lead to a dramatic decrease in mishandling and errors, ultimately contributing to a more reliable and efficient industrial process.
The future of gland valve technology is poised for significant innovation, driven by advancements in materials, automation, and smart technologies. With a growing emphasis on sustainability and efficiency, manufacturers are exploring the use of corrosion-resistant and lightweight materials to enhance the durability and performance of gland valves. This shift not only extends the lifespan of these valves but also reduces maintenance costs, aligning with industry-wide goals of minimizing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
Furthermore, the integration of smart technology into gland valve systems is revolutionizing their operation. Sensors that provide real-time monitoring and data analytics enable predictive maintenance, allowing operators to anticipate issues before they escalate. This proactive approach not only enhances safety but also optimizes system performance, ensuring that gland valves function effectively under varying operational conditions. As industries increasingly adopt automation, the demand for advanced control systems that can seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure will also drive innovation in gland valve technology. This convergence of smart technology with traditional valve mechanisms signifies a transformative transition toward more intelligent and responsive industrial systems.